Power Locks Explained – The Future of Keyless Industrial Safety

Industrial environments are complex ecosystems where heavy machinery, high-voltage equipment, and intricate workflows coexist. In such high-stakes settings, the margin for error is razor-thin. Ensuring the safety of personnel and the security of assets is not just a regulatory requirement; it is an operational imperative.
Traditional locking mechanisms—heavy padlocks and brass keys—have been the standard for decades. While effective to a point, they come with inherent vulnerabilities. Keys get lost, duplicated without authorization, or broken inside cylinders. In an emergency, fumbling for the right key on a chaotic ring can cost valuable seconds.
Enter the power lock. This modern, keyless solution is transforming how industries approach access control and safety. By eliminating the physical key, power locks remove a significant layer of friction and risk from industrial operations.
This guide explores what power locks are, how they function, and why they are becoming the preferred choice for forward-thinking facilities. We will also discuss how our range of commercially available power locks can upgrade your safety protocols today.
What Is a Power Lock?
A power lock is an advanced locking mechanism designed to secure industrial machinery, electrical panels, and restricted areas without the use of a traditional mechanical key. Instead of relying on a physical object that can be lost or stolen, power locks typically utilize mechanical friction, magnetic forces, or electronic signals to secure components.
How Power Locks Work
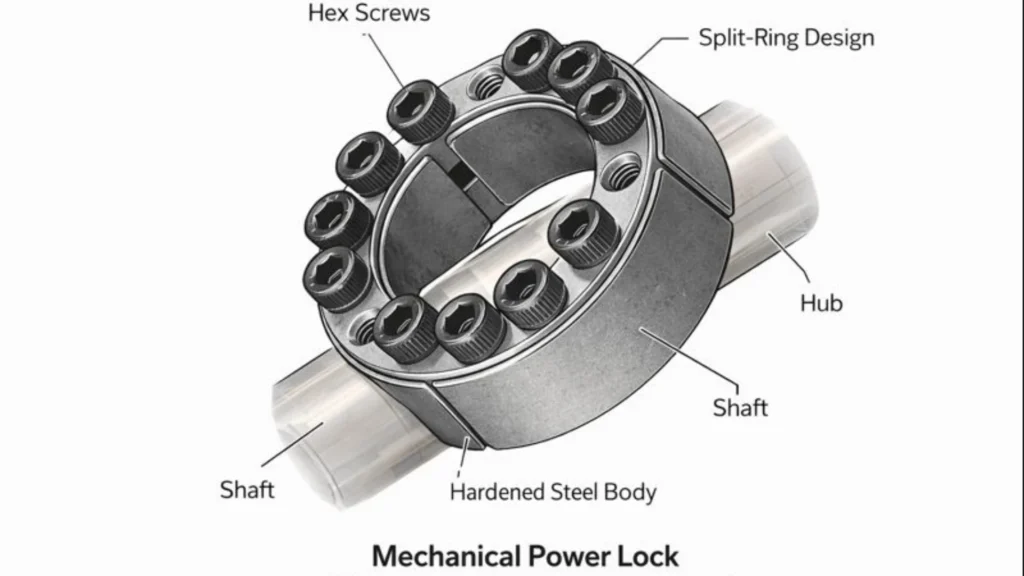
The mechanics of a power lock depend on the specific type, but the core principle remains consistent: establishing a secure hold that can be easily released by authorized personnel or specific conditions.
In mechanical keyless locking devices (often used in power transmission), the lock uses a series of tapered rings. When tightened, these rings expand to create a robust interference fit between a shaft and a hub. This eliminates the need for keyways or splines, which are often weak points in mechanical design.
In the context of access control (like securing a cabinet or gate), power locks may refer to electromechanical locks or solenoid locks. These devices remain locked when energized (fail-safe) or locked when de-energized (fail-secure), controlled by a keypad, RFID card, or remote switch.
The Difference Between Power Locks and Traditional Industrial Locks
The primary distinction lies in the actuation method. A traditional industrial lock requires the physical insertion and rotation of a unique metal key. A power lock relies on internal mechanisms—whether mechanical expansion or electronic actuation—to maintain security. This fundamental difference drastically reduces wear and tear, eliminates “key management” headaches, and often provides a higher torque capacity in mechanical applications.
Why Industrial Safety Needs Advanced Locking Systems
Safety risks in industrial environments are evolving. As machinery becomes more powerful and automated, the protective measures surrounding them must adapt.
Common Safety Risks
Accidents often occur during maintenance or unplanned downtime. If a machine isn’t properly isolated, or if an unauthorized person gains access to a high-voltage panel, the consequences can be fatal. “Stored energy” is a silent killer in manufacturing; secure locking systems are the only barrier between a worker and a hazardous release of energy.
The Role of Industrial Locks in Accident Prevention
Locks serve as the final line of defense. They ensure that safety guards remain closed during operation and that energy sources are isolated during maintenance. However, a lock is only effective if it is used correctly. Traditional locks can be bypassed if a key is available to the wrong person.
The Importance of Certified Solutions
Using non-standard or residential-grade locks in an industrial setting is a recipe for disaster. Industrial locks must withstand vibration, dust, moisture, and extreme force. Relying on certified, reliable locking solutions ensures that the device won’t fail when it matters most.
What Are Keyless Locking Devices?
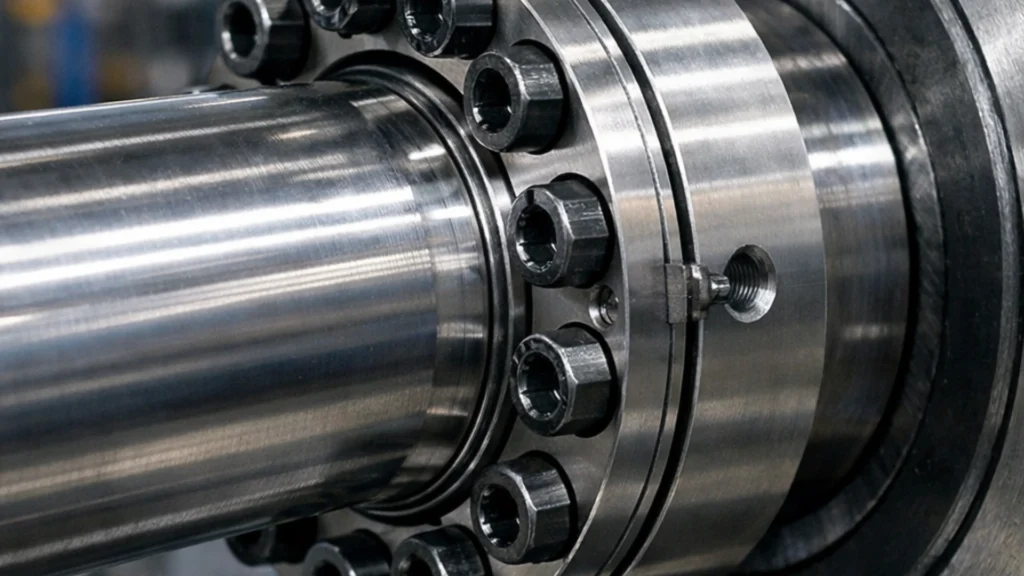

Keyless locking devices are a subset of power locks specifically designed for mechanical power transmission. They connect hubs (like gears, pulleys, or sprockets) to shafts.
Types of Keyless Locking Systems
- Mechanical Shrink Discs: These are external locking devices. They are placed over a hub and, when tightened, compress the hub onto the shaft.
- Internal Locking Assemblies: These fit inside the hub bore. As screws are tightened, the device expands radially, creating high pressure against the shaft and the hub.
- Hydro-Mechanical Locks: These use hydraulic pressure to create the interference fit, offering incredibly fast installation and removal.
Benefits Over Conventional Keyed Locks
Conventional keyed connections (using a keyway cut into the shaft) create “notch effects.” These notches concentrate stress, making the shaft prone to cracking under heavy loads or reversing torque. Keyless locking devices distribute the load evenly across the entire surface area of the connection. This means:
- Higher Torque Transmission: No weak points means the connection can handle more power.
- Zero Backlash: The fit is tight and precise, essential for high-speed machinery.
- Easy Adjustability: You can position the hub anywhere on the shaft without needing to cut a new keyway.
How Power Locks Improve Industrial Safety
Transitioning to power locks isn’t just about mechanical efficiency; it is a direct upgrade to your safety culture.
Elimination of Lost or Duplicated Keys
Key control is a logistical nightmare for large facilities. If a master key goes missing, the security of the entire facility is compromised, often requiring expensive re-keying. Power locks and keyless devices remove this variable entirely. There is no physical key to lose, steal, or copy.
Better Access Control and Authorization
With electronic power locks, access can be granted or revoked instantly. You can track exactly who opened a specific cabinet and when. In mechanical applications, keyless locking devices prevent “jury-rigged” repairs where workers might use improper keys or shims to fix a loose connection, creating a safety hazard.
Faster Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Time pressure is a major cause of safety shortcuts. If a worker has to hunt for a key to lock out a machine, they might be tempted to skip the step. Power lock systems streamline this process. Many modern systems integrate with automated control systems, ensuring that machinery cannot be energized until the lock is engaged.
Improved Safety Compliance
Regulatory bodies like OSHA have strict standards regarding the control of hazardous energy. utilizing advanced locking mechanisms demonstrates a commitment to “best available technology,” helping your facility stay compliant and avoid costly fines.
Power Lock Applications in Industrial Environments

Versatility is one of the strongest attributes of power locks. They are found across a wide spectrum of sectors.
Manufacturing Plants
In assembly lines, keyless locking assemblies secure conveyor pulleys and robotic arms. They ensure that these high-speed components don’t slip or fail, which could send heavy parts flying and injure workers.
Electrical Panels and Control Cabinets
Electronic power locks are ideal for securing high-voltage cabinets. They can be integrated with sensors that detect if the cabinet is hot, physically preventing the door from opening until the power is confirmed off.
Heavy Machinery and Restricted Zones
For heavy crushers, presses, and mills, power locks provide the high-torque connection needed to transmit massive amounts of energy safely. They also secure the perimeter gates, ensuring that the machine shuts down immediately if a gate is forced open.
Industrial Safety and Maintenance Operations
During maintenance, ease of removal is critical. Traditional keyed shafts can rust and seize, forcing maintenance crews to use torches or sledgehammers to remove parts—a dangerous practice. Keyless power locks can be released by simply loosening screws, making maintenance safer and faster.
Power Industry Lock Solutions We Offer
The power generation and distribution sector has unique needs. Equipment here faces high voltage, extreme weather, and continuous operation. A lock failure in a substation isn’t just an inconvenience; it can cause a blackout.
Importance of Power Locks in the Power Industry
In substations and power plants, security is paramount to prevent sabotage or accidental public access. Furthermore, the internal machinery (turbines, generators) requires the robust connection that only keyless locking devices can provide.
Use Cases in Substations and Electrical Facilities
- Transformer Cabinets: Securing access to sensitive controls.
- Generator Shafts: Connecting the massive rotors in turbines without stress-inducing keyways.
- Switchgear: Ensuring reliable mechanical interlocks.
Overview of Power Locks We Sell
We supply a curated range of power locks specifically engineered for the rigors of the power industry. Our inventory includes:
- High-Corrosion Resistant Locks: Designed for outdoor substations exposed to rain and snow.
- Heavy-Duty Locking Assemblies: Capable of handling the immense torque of industrial generators.
- Smart Interlocks: Solutions that integrate with SCADA systems for remote monitoring.
We prioritize quality and durability above all else. When you source from us, you are getting equipment tested to meet stringent safety standards.
Why Buy Power Locks from Us?
Choosing a supplier for safety-critical components is a decision that requires trust. Here is why industry leaders partner with us for their locking needs.
High-Quality Industrial-Grade Materials
We do not cut corners with materials. Our power locks are manufactured using high-grade steel alloys and corrosion-resistant coatings. They are built to last in environments where standard commercial locks would fail within weeks.
Reliable and Tested Keyless Locking Devices
Every product we supply undergoes rigorous testing. We ensure that our locking assemblies meet rated torque specifications and that our access locks function reliably under continuous use.
Suitable for Harsh Environments
From the dusty heat of a cement plant to the humid, corrosive air of a coastal power station, our locks are rated for the environment they serve. We understand that “industrial use” means taking a beating and continuing to perform.
Expert Support and Product Guidance
Not sure if you need a shrink disc or an internal locking assembly? Unsure about the voltage requirements for an electromechanical lock? Our team of experts is here to help. We don’t just sell parts; we provide technical guidance to ensure you get the right solution for your specific machine or facility.
Easy Ordering and Dependable Supply
Downtime is expensive. We maintain a robust inventory to ensure that we can ship critical components quickly. Our ordering process is streamlined to get your facility back up and running—or secured—as fast as possible.
Power Lock vs. Traditional Industrial Locks
Is it worth the upgrade? Let’s look at the comparison.
Security Comparison
Traditional locks are vulnerable to picking, drilling, and key theft. Power locks remove the keyhole vulnerability. Keyless mechanical locks provide a stronger physical connection than keyed shafts, which can shear under load.
Maintenance and Usability
Keyed connections wear out over time, leading to “wobble” and eventual failure. Keyless power locks are self-centering and do not wear the shaft. They are easier to install and easier to remove, saving hours of labor during maintenance shutdowns.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
While the upfront cost of a power lock or keyless assembly may be higher than a simple keyed shaft or padlock, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is lower. You save on:
- Machining costs (no keyways to cut).
- Maintenance labor.
- Replacement costs for worn shafts.
- Re-keying costs for lost keys.
Why Modern Power Locks Are a Better Investment
Investing in power locks is an investment in uptime and safety. The reduction in maintenance headaches alone often pays for the upgrade within the first year of operation.
How to Choose the Right Power Lock for Your Facility
Selecting the correct device is critical for safety and performance. Consider these factors:
Lock Type and Application Needs
Are you securing a door or a rotating shaft? If it’s a shaft, what is the torque requirement? If it’s a door, do you need remote access control?
Environmental Conditions
Will the lock be exposed to chemicals, water, or extreme temperatures? Stainless steel options are available for food processing or marine environments.
Industry Compliance Requirements
Ensure the lock meets the specific standards of your industry (e.g., NEMA ratings for electrical enclosures or specific ANSI standards for machine safety).
Getting Expert Help Before Purchase
Don’t guess when it comes to safety. Contacting a supplier who understands the technical specifications can save you from buying an incompatible or under-rated component.
Where to Buy Reliable Power Locks
The safety of your workforce and the efficiency of your machinery depend on the quality of your equipment. Buying from a big-box retailer or an unverified online marketplace poses significant risks. You need a partner who understands industrial requirements.
Ohiorollerchain specializes in supplying top-tier power locks and keyless locking devices. Whether you are retrofitting an old plant or outfitting a new facility, we have the inventory and the expertise to support you.
Ready to upgrade your facility’s safety and efficiency? Contact our team today for pricing, technical specifications, and personalized support. Let us help you secure your operations with the best power locks on the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a power lock used for?
A power lock is used to secure industrial components without a traditional key. In mechanical transmission, it connects hubs to shafts securely. In access control, it secures doors and panels using electronic or magnetic force.
Are power locks safer than traditional industrial locks?
Yes, generally. They eliminate the risks associated with lost keys and provide stronger mechanical connections that are less prone to failure under heavy loads.
Can power locks be used in the power industry?
Absolutely. They are essential in the power industry for securing high-voltage enclosures and for connecting heavy turbine and generator components where reliability is critical.
Do you sell power locks for industrial use?
Yes, we supply a wide range of industrial-grade power locks and keyless locking devices suitable for manufacturing, energy, and heavy industry.
How can I buy a power lock from your company?
You can browse our catalog online or contact our sales team directly. We can assist with product selection to ensure you get the exact specification needed for your application.
Conclusion
The shift from traditional keyed systems to power locks represents a significant leap forward for industrial safety and efficiency. By eliminating physical keys and utilizing advanced mechanical and electronic technologies, power locks offer superior security, reduced maintenance, and better compliance with safety standards.
Whether you are looking to secure a high-voltage substation or optimize a manufacturing conveyor, the right locking system makes all the difference. Don’t let outdated technology compromise your operations.
Take the next step in securing your facility. Contact us today to discuss your needs and buy reliable, industrial-strength power locks designed for the modern world.

